Manage Test Automation Servers
Unavailability for SquashTM Cloud
Users of the SquashTM Cloud offer cannot add or delete test automation servers. The name, URLs, description, and authentication cannot be modified either.
Add, modify, and delete a Test Automation Server
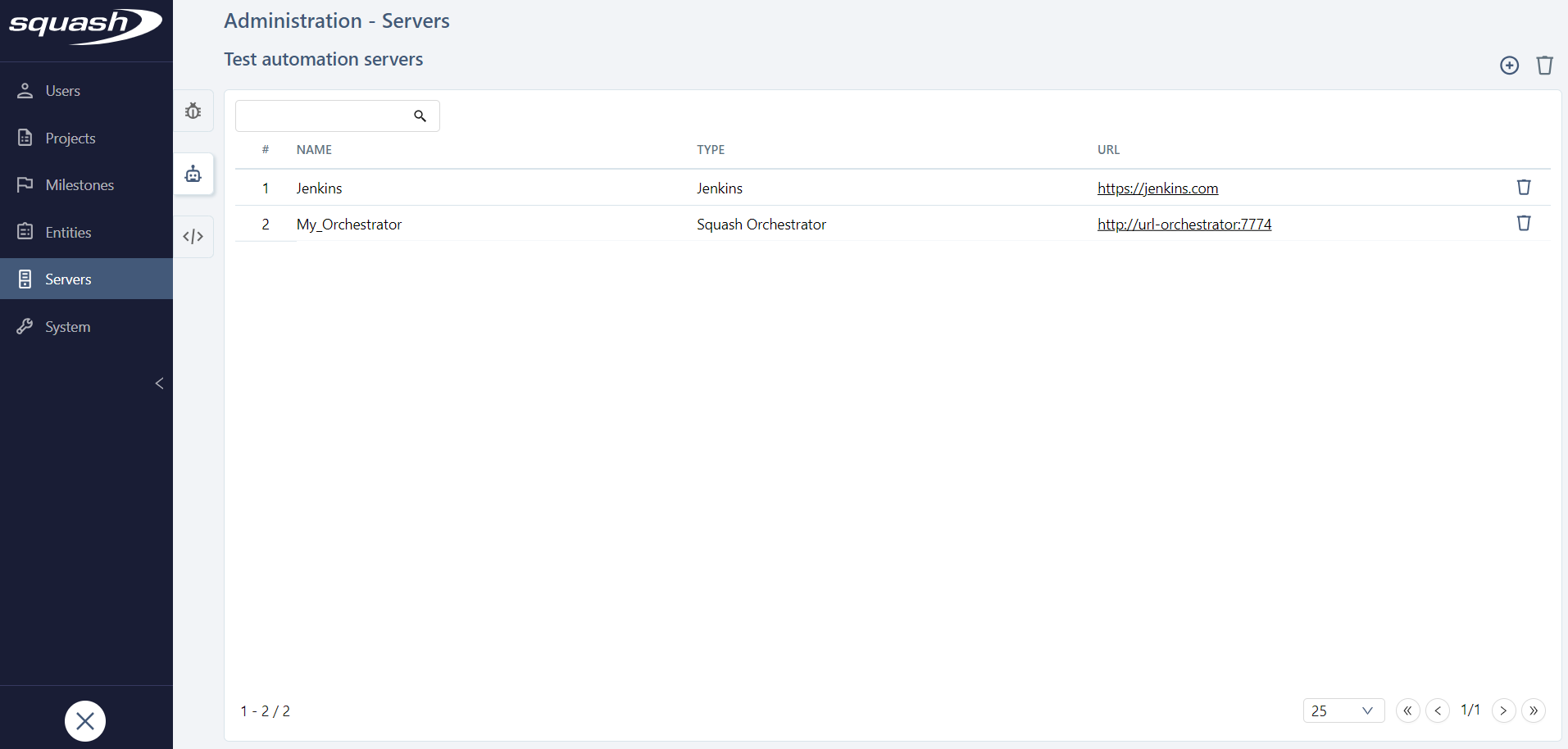
SquashTM can connect to two different types of test automation servers: SquashTM Orchestrator to automate tests with SquashTM Orchestrator and Jenkins to automate tests with Squash TF.
To add and configure a test automation server, go to the Administration workspace, then click on Servers > Test automation servers.
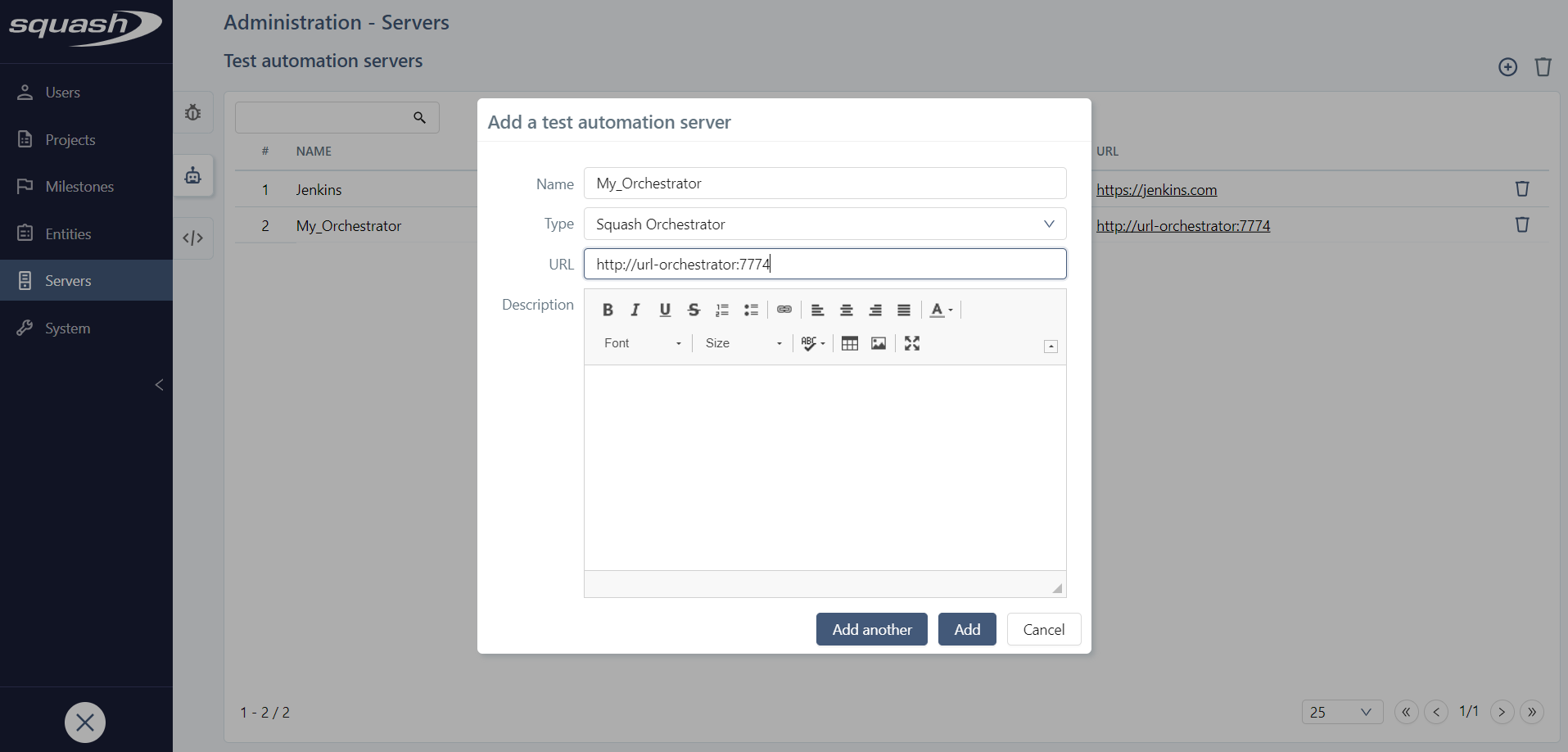
When you create a server, you must set the server's Name, Type, and URL (the URL should be as short as possible).
Warning
Deleting a test automation server associated with at least one project or execution deletes the links to the results and execution reports, as well as the automation script associations with the test cases. However, you can still access automated test cases executions. This action cannot be undone.
Configure a SquashTM Orchestrator test automation server
Configure the connection to SquashTM Orchestrator
For SquashTM to communicate with SquashTM Orchestrator, the following URLs must be configured:
- Receptionist URL: it is the URL entered when adding the server in SquashTM. It is used to launch automated tests with SquashTM Orchestrator;
- Observer URL: it is used to retrieve SquashTM Orchestrator information. If this URL is not configured, the receptionist URL is used;
- Event bus URL: event bus allows the passage of subscription and publication information to various services of SquashTM Orchestrator. If this URL is not configured in SquashTM, the receptionist URL is used;
- Killswitch URL: killswitch allows to cancel an in-progress workflow. If this URL is not configured, the receptionist URL is used.
There are two main types of deployment configuration:
- SquashTM Orchestrator is installed behind a reverse proxy: receptionist URL, observer URL, event bus URL, and killswitch URL are identical and communicate with SquashTM via the same port.
Example:- Receptionist URL:
https://mysquashorchestrator.com - Observer URL:
https://mysquashorchestrator.com - Event bus URL:
https://mysquashorchestrator.com - Killswitch URL:
https://mysquashorchestrator.com
- Receptionist URL:
- SquashTM Orchestrator is not installed behind a reverse proxy: receptionist URL, observer URL, event bus URL, and killswitch URL are different. Default exposed ports are
7774for the receptionist,7775for the observer,38368for the event bus, and7776for the killswitch. The base URL can also differ.
Example:- Receptionist URL:
http://127.0.0.1:7774 - Observer URL:
http://127.0.0.1:7775 - Event bus URL:
http://127.0.0.1:38368 - Killswitch URL:
http://127.0.0.1:7776
- Receptionist URL:
Learn more
To learn more about SquashTM Orchestrator installation and configuration, visit the installation guide.
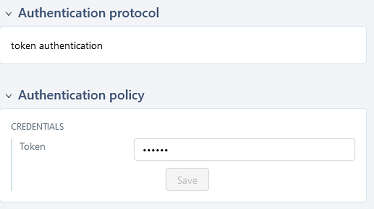
For the server to work, an authentication token, generated from SquashTM Orchestrator, is needed.
Info
With SquashTM Orchestrator, there must be a token for the automated test to execute correctly from SquashTM. Even if the automation server does not require you to authenticate yourself, you must still enter any value for the token in SquashTM. The token can be configured at project level.
Consultation page of a SquashTM Orchestrator test automation server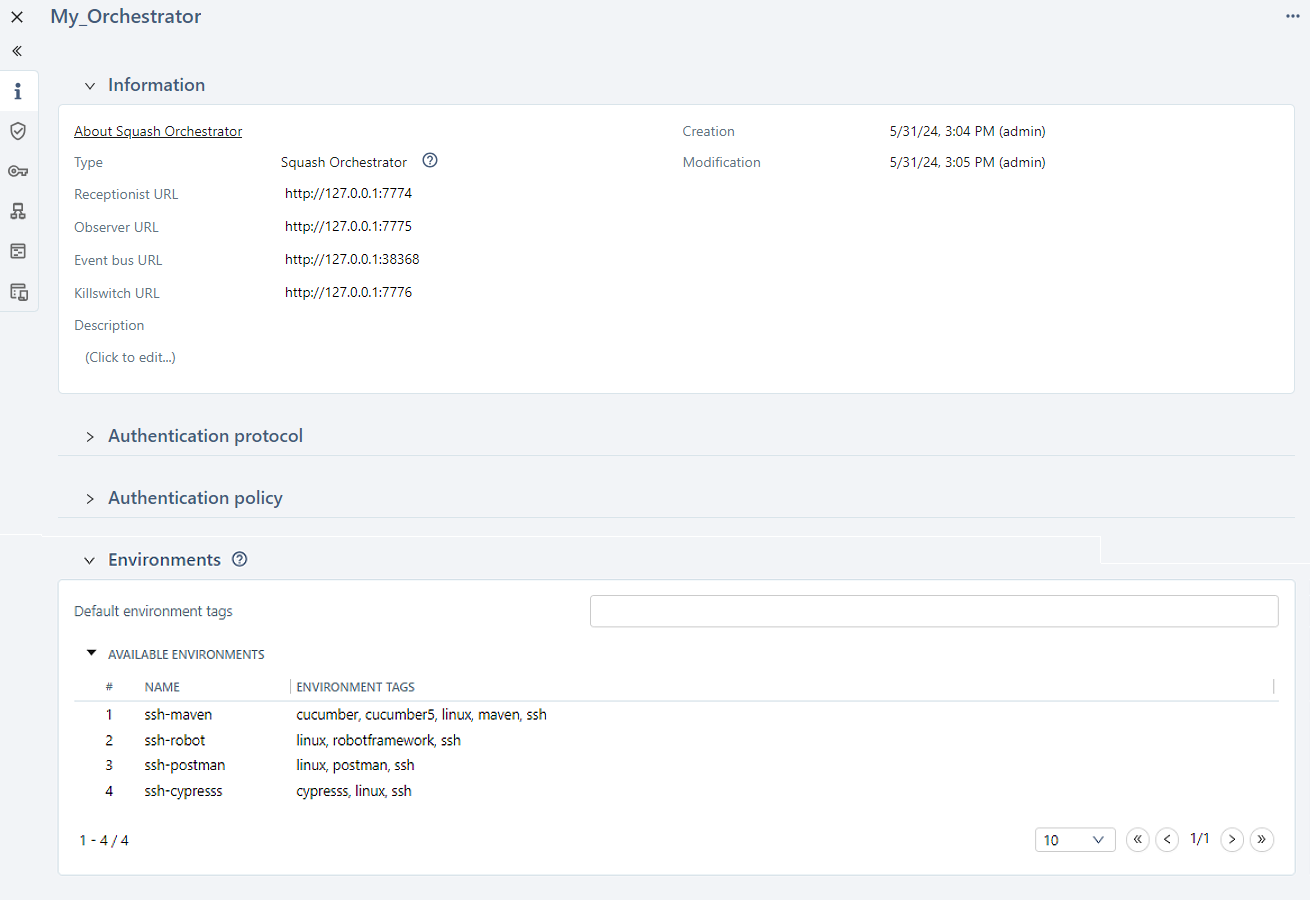
Trouble shooting - Accessibility of SquashTM Orchestrator
It is possible to check that the connection to the SquashTM Orchestrator (from the server hosting SquashTM) works correctly by querying it, for example by asking for the list of execution environments:
curl --header "Authorization: bearer <token>" <Observer URL>/channels
<token>is the SquashTM Orchestrator authentication token.<Observer URL>is the Observer URL.
The response should be something like the following:
{"apiVersion":"v1","code":200,"details":{"items":[{"apiVersion":"opentestfactory.org/v1alpha1","kind":"Channel","metadata":{"channelhandler_id":"907f43e2-b5a0-4594-a1c7-31f6bf667b38","name":"dummy.example.com","namespaces":"default"},"spec":{"tags":["ssh","linux"]},"status":{"currentJobID":null,"lastCommunicationTimestamp":"2022-09-16T12:18:01.640489","phase":"IDLE"}}]},"kind":"Status","message":"Known channels","metadata":{},"reason":"OK","status":"Success"}
The SquashTM Docker image does not contain curl. You can use wget instead:
docker exec <SquashTM container> wget --header="Authorization: bearer <token>" -O - <Observer URL>/channels
<SquashTM container>is the name of the container.<token>is the SquashTM Orchestrator authentication token.<Observer URL>is the Observer URL.
The response should be something like the following:
Connecting to 172.17.0.1:7775 (172.17.0.1:7775)
writing to stdout
- 100% |********************************| 464 0:00:00 ETA
written to stdout
{"apiVersion":"v1","code":200,"details":{"items":[{"apiVersion":"opentestfactory.org/v1alpha1","kind":"Channel","metadata":{"channelhandler_id":"907f43e2-b5a0-4594-a1c7-31f6bf667b38","name":"dummy.example.com","namespaces":"default"},"spec":{"tags":["ssh","linux"]},"status":{"currentJobID":null,"lastCommunicationTimestamp":"2022-09-16T12:18:01.640489","phase":"IDLE"}}]},"kind":"Status","message":"Known channels","metadata":{},"reason":"OK","status":"Success"}
Define a default execution environment
Executions environments in SquashTM Orchestrator can be declared through ssh or an agent.
The characteristics of each execution environment are indicated with tags: OS, browser…
Learn more
For more information on environment tags use cases, please see Pilot automated tests from SquashTM.
The Environments block lists the available environments with their tags. It can be used to define default environment tags.
The Available environments table contains the list of environments with their tags.
This information is returned in real time by SquashTM Orchestrator. Displayed environments depend on the token configured in the Authentication policy and its permissions on each environment.
The Default environment tags field can be used to filter the Available environments table: only the environments having all the tags present in that field will be listed.
When running automated tests, these tags are offered by default to the user (he/she can modify them) to target an execution environment that matches the selected values.
Learn more
Token and default environment tags can also be defined on the projects linked to the SquashTM Orchestrator test automation server. In this case, the project's values are selected by default when running automated tests. To learn more, visit the page Associate a SquashTM Orchestrator test automation server to a project.
Associate environment variables and define their default value
Environment variables can be used to define various settings such as credentials, environment type (e.g. production or pre-production), Git branch, the browser for testing… Unlike the environment tags that are returned by SquashTM Orchestrator, environment variables must be created in SquashTM.
Learn more
For more information on environment variables use cases, please see Pilot automated tests from SquashTM.
The Environment variables block allows you to associate environment variables previously created in Administration > Entities > Environment variables, and to define their default value.
To associate an environment variable with the test automation server, click on ![]() and select the variable(s) to associate.
and select the variable(s) to associate.
Once the environment associated, it is possible to define a default value. This value can be redefined at the project level. Depending on the environment variable type, different characters are authorized. When running automated tests, this value is offered by default to the user, but they can modify it.
To dissociate one or multiple environment variables from a test automation server, click on ![]() .
.
Set up an additional configuration for the automated execution server
Warning
Additional configuration management is available with SquashTM Ultimate license and SquashTM Premium plugin.
The additional configuration allows data to be sent directly from SquashTM to the orchestrator when a workflow is created (hooks, environment variables, resources, etc.).
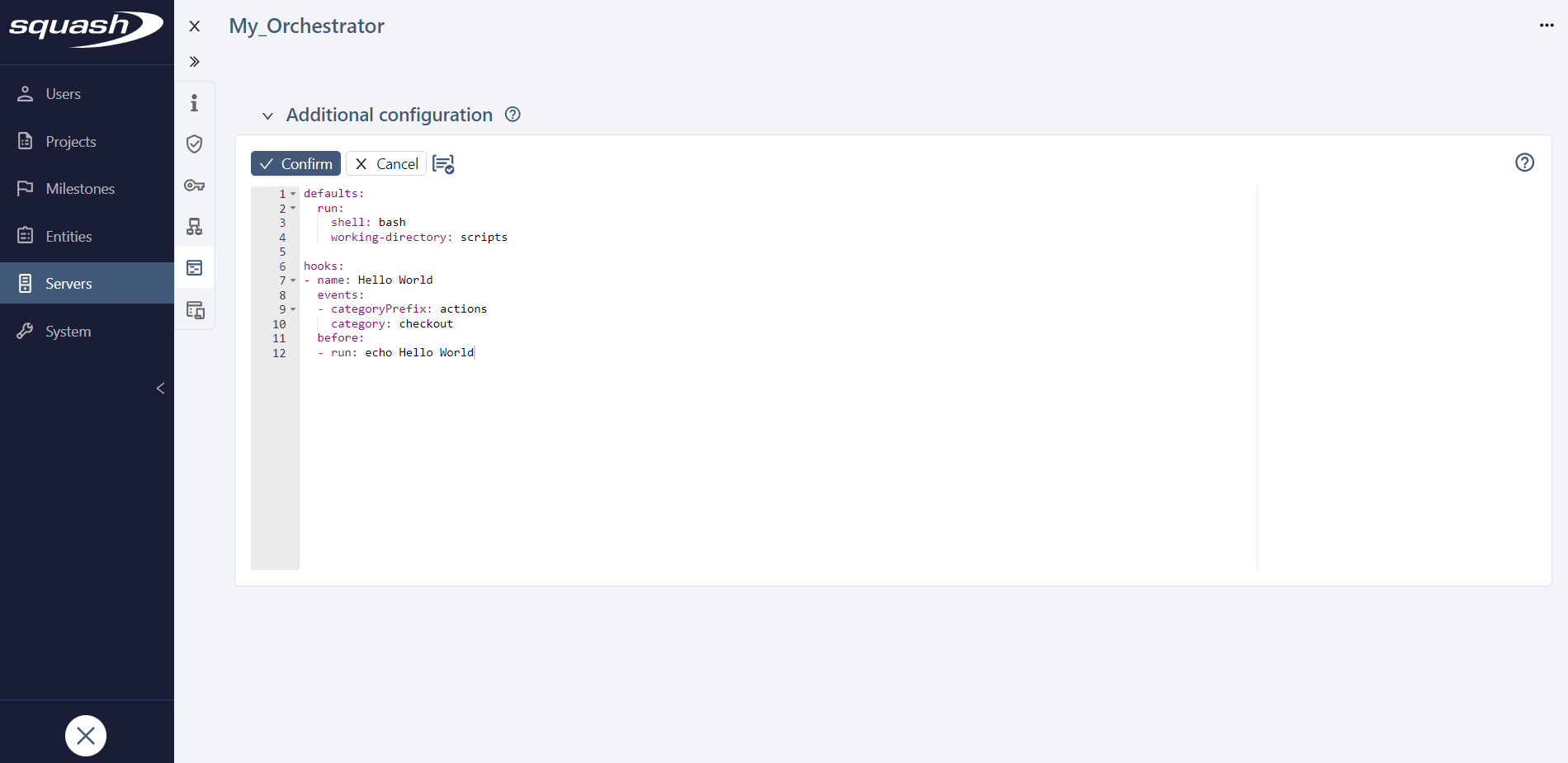
To do this, a dedicated space is available for declaring a YAML or JSON script with colouring and syntax checking.
Click in the field to edit a script. Several buttons then appear above the script, allowing you to:
- confirm the changes made, you can also use the keyboard shortcut Ctrl+Alt+S;
- cancel changes made since the last save and return to read-only mode;
- check the script syntax.
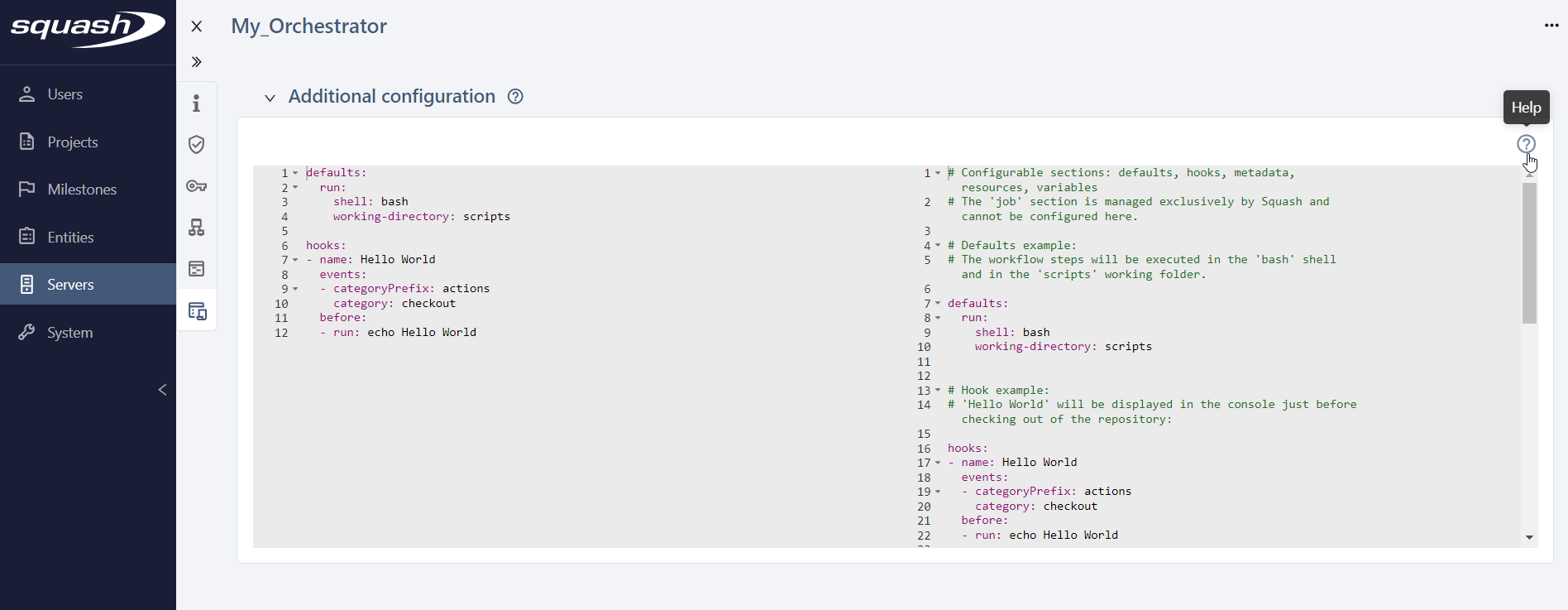
The  button displays a help panel for writing additional configuration scripts, showing examples of hooks, metadata, resources, and variables.
button displays a help panel for writing additional configuration scripts, showing examples of hooks, metadata, resources, and variables.
Learn more
To learn more about additional workflow configuration, consult the SquashTM Orchestrator documentation.
Configure a Squash TF test automation server
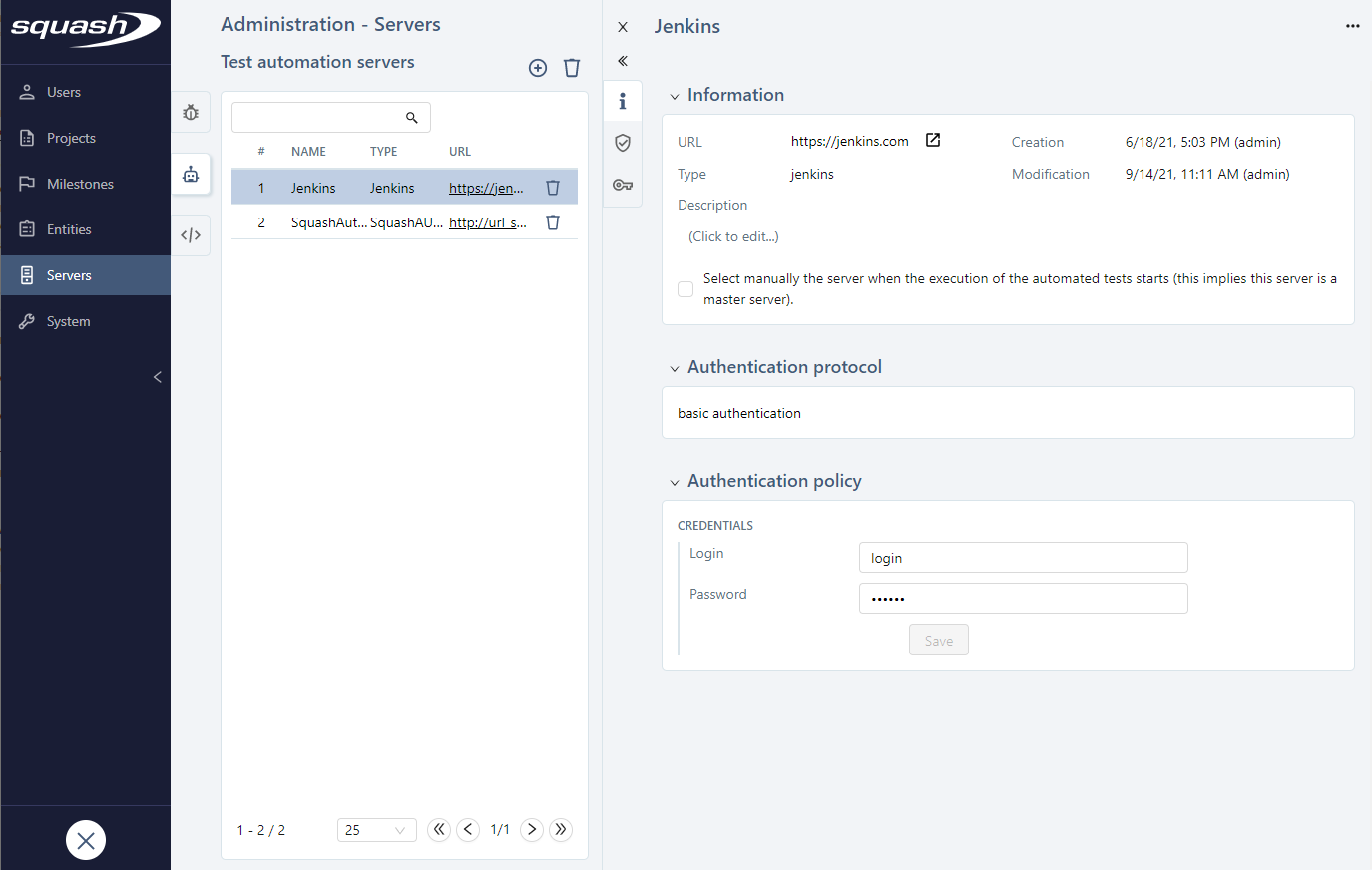
When you add a Jenkins automation server, the checkbox Select manually the server when the execution of the automated tests starts (this implies this server is a master server) enables you to choose the execution server at the start of the tests when using master servers with secondary servers.
For the server to work, you also must enter credentials: Jenkins login and password.
Consultation page of a Jenkins test automation server