Automation with Robot Framework
Configuration of the execution environment
In order to retrieve the SquashTM parameters, the squash-tf-services Python library must be present.
It can be installed with the command:
pip install squash-tf-services
Test reference in SquashTM
In order to bind a SquashTM test case to a Robot Framework automated test, the content of the Automated test reference field of the Automation block of a test case must have the following format:
[repository]/[file]#[test_case]
or[repository]/[file]
(The reference contains zero or one # character.)
with:
[repository]: Name of the Git repository.[file]: Path and name of the Robot Framework test, from the root of the project (with the.robotextension).
It is possible to not indicate a.robotfile name and, instead, only define the name of a folder. In this case, all the.robotfiles of this folder and its sub-folders will be executed.[test_case]: Name of the test case to execute in the.robotfile(s).
This parameter is optional, i.e. it may be absent.
Determination of the result of the test case
If a test case [test_case] is not specified, the result of the SquashTM test case is calculated by taking into account the individual results of each test in the file/folder [file]:
- If at least one test has an Error status (in case of a technical issue), the status of the execution will be Blocked.
- If at least one test fails functionally and none of the other ones has an Error status, the status of the execution will be Failed.
- If all tests succeed, the status of the execution will be Success.
Nature of the exploitable SquashTM parameters
The exploitable SquashTM parameters will differ depending on whether you're using the Community/Premium or Ultimate version of SquashTM.
Here is a table showing the exploitable parameters (these parameters are transmitted as test parameters, see below, SquashTM does not generate global parameters):
| Nature | Key | Community/Premium | Ultimate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Name of the dataset | DSNAME | ✅ | ✅ |
| Dataset parameter | DS_[name] | ✅ | ✅ |
| Execution ID | TC_EXECUTION_ID | ❌ | ✅ |
| Test case reference | TC_REFERENCE | ✅ | ✅ |
| Test case internal UUID | TC_UUID | ✅ | ✅ |
| Test case custom field | TC_CUF_[code] | ✅ | ✅ |
| Iteration custom field | IT_CUF_[code] | ❌ | ✅ |
| Campaign custom field | CPG_CUF_[code] | ❌ | ✅ |
| Test suite custom field | TS_CUF_[code] | ❌ | ✅ |
Legend:
[code]: Value of the "Code" of a custom field[name]: Name of a datasset
As indicated, SquashTM adds a prefix to the code of the transmitted custom field. Make sure to take it into account.
Availability of the execution ID
TC_EXECUTION_ID is only available with Squash TM 8.0 or later.
Parameters usage
It is possible, when running Robot Framework tests, to exploit parameters within it. A parameter can be a test parameter or a global parameter. SquashTM transmits only test parameters. Test parameters and global parameters can be used in the case of a launch from a CI/CD pipeline with the robotframework/params action.
In order to achieve this, you have to follow these steps:
Import the squash-tf-services library in the
Settingssection of the.robotfile:Library squash_tf.TFParamServiceYou can then retrieve the value of a parameter by calling one of the following keywords:
This keyword retrieves the value of a global parameter.${value}= Get Global Param key ${value}= Get Global Param key default_value
If it exists, its value is assigned to${value}.
Otherwise the default value is assigned to${value}; if no default value was provided,Noneis used.
Example:${parameter}= Get Global Param target_base_url http:localhost:8080/sut/
This keyword retrieves the value of a test parameter.${value}= Get Test Param key ${value}= Get Test Param key default_value
If it exists, its value is assigned to${value}.
Otherwise the default value is assigned to${value}; if no default value was provided,Noneis used.
Example:${login}= Get Test Param TC_CUF_login test_user
This keyword combines both types of parameters.${value}= Get Param key ${value}= Get Param key default_value
If a test parameter exists, its value is assigned to${value}.
Otherwise, if a global parameter exists, its value is assigned to${value}.
Otherwise, the default value is assigned to${value}; if no default value was provided,Noneis used.
Example:${login}= Get Param login test_user
Example
Below is an example of a Robot Framework test file and the corresponding SquashTM test case automation:
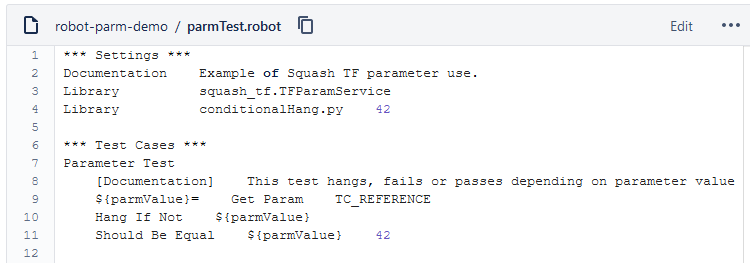
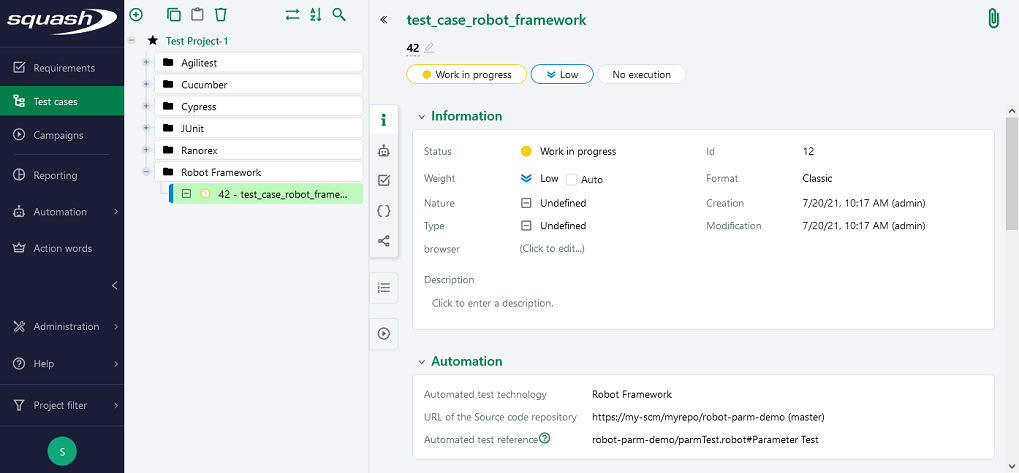
Adding parameters to the test launch command line
You can pass additional parameters to the robot command using the ROBOTFRAMEWORK_EXTRA_OPTIONS environment variable. Here is an example of how to define an environment variable in SquashTM and associate it with the orchestrator.
Some parameters are already defined in the robot command used to launch tests:
robot \
$ROBOTFRAMEWORK_EXTRA_OPTIONS \
--nostatusrc --listener "allure_robotframework;." \
--test {testcase_name} "{datasource_path}"
You must avoid passing, via the ROBOTFRAMEWORK_EXTRA_OPTIONS variable, the command line parameters that conflict with the parameters already used, or the parameters that impact the generation or alter the path of the reports expected by the orchestrator (view the report list).
Non-support of the space character on Linux
SquashTM Orchestrator currently does not support the space character () in the ROBOTFRAMEWORK_EXTRA_OPTIONS environment variable for tests executed in a Linux execution environment.
Supported versions
SquashTM has been validated with the following versions of Robot Framework. More recent versions should work properly.
| Testing Technology | Version |
|---|---|
| Robot Framework | 6.1.1 |