Configure a Project
To configure a project, in the Administration workspace, click on the "Projects" submenu. Click on your desired project to display its consultation page.
Info
Only an administrator or project leader can configure a project.
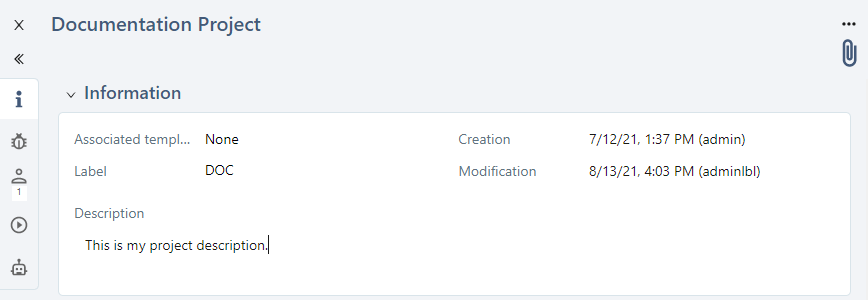
The "Information" anchor  enables you to enter and view the project's overall data.
enables you to enter and view the project's overall data.
Configure a Bugtracker
You can configure the link with the bugtracker from the Bugtracker anchor  .
.
To configure a bugtracker for a project, the corresponding server must be declared beforehand by an administrator in the "Servers" submenu. Then, you can select the bugtracker in a drop-drown list to associate it with the project.
In the "Project Name" field, enter the name of the project as it is configured in the third-party tool. Make sure that the name is spelled correctly, with the correct uppercase and lowercase letters. In this field, you can associate multiple projects if you want. When reporting issues, you can choose the project in which the issue must be reported.
![]()
Info
For some bugtrackers such as GitLab and Azure DevOps, the "Project name" field is replaced by "Project path":
- for GitLab, you must enter the project path as it appears in the URL, and replace the spaces by "-". Ex: <group-name or owner-name>/<sub-group-name>/<project-name>
- for Azure DevOps, you must enter the project path and keep the spaces. Ex: <organization-name>/<project name>
Focus
During the execution, if the name of the project entered does not exist, or if it is spelled incorrectly, an error message appears when you report an issue.
Learn More
To learn more about how to create a bugtracking type of server, please visit the page Manage bugtrackers and synchronization servers
Manage Project Permissions
You can manage a project's permissions from the Permissions anchor  . You can give permissions to users or teams on the project.
. You can give permissions to users or teams on the project.
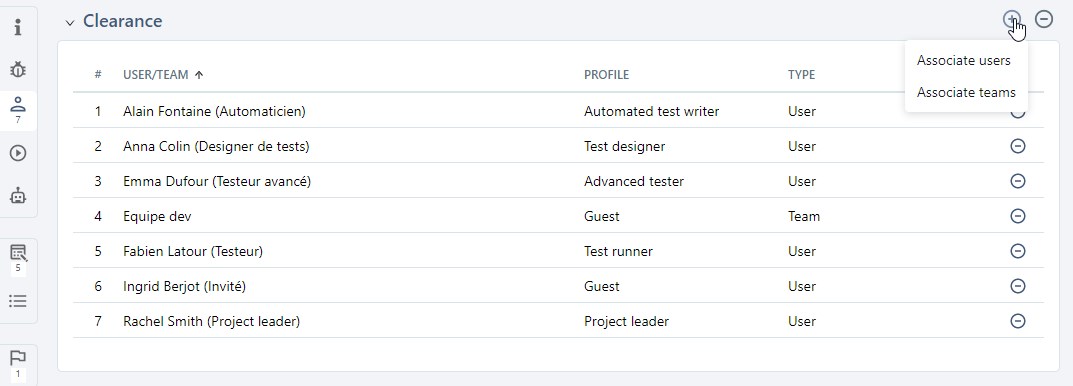
The button ![]() enables you to remove one or multiple permissions on the project.
enables you to remove one or multiple permissions on the project.
You can edit user or team profiles directly in the table by clicking on their profile.
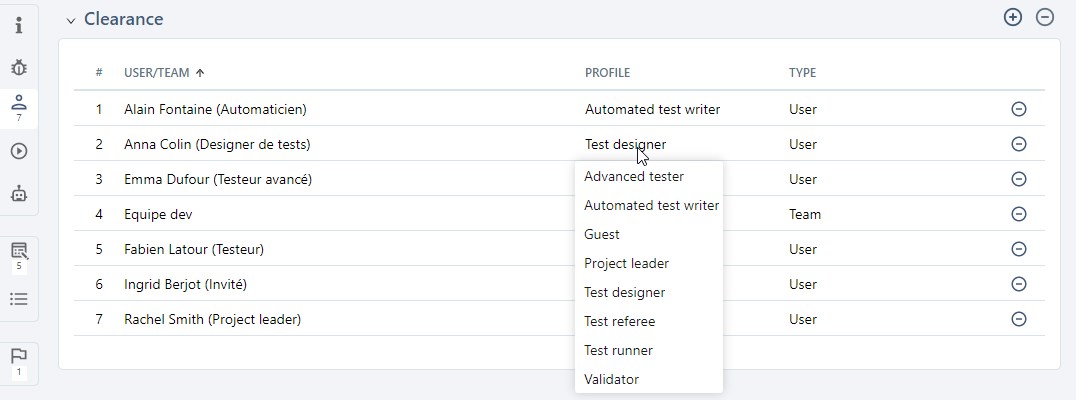
A user or team can have different profiles for different projects.
Learn More
To learn more about different profiles and permissions of Squash TM workspaces, please visit the page: Give permissions
Define Execution Preferences
To activate some features regarding test case executions, click on the Executions anchor  :
:
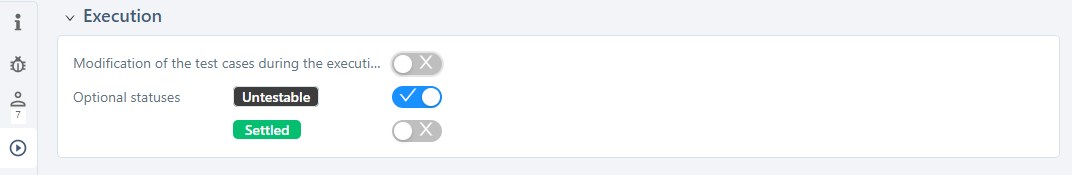
- Authorize the modification of test cases during their execution;
- Activate/Deactivate their execution status during their execution;
- Activate/Deactivate the execution status "Untestable";
- Activate/Deactivate the execution status "Settled".
Only the status "Untestable" is activated by default.
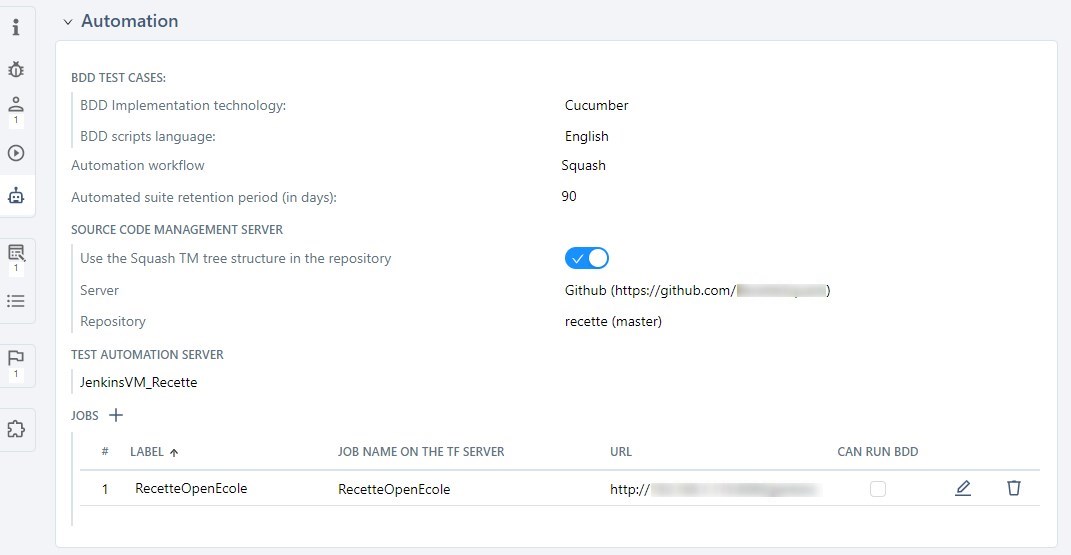
Configure the Project's Automation
The Automation button  enables you to configure the automation of the project.
enables you to configure the automation of the project.
From this block, you can:
- Select the implementation technology of BDD test cases;
- Select the language of BDD scripts;
- Activate an automation workflow (Squash or Jira)
- Configure a retention period for automated suites;
- Associate a source code management server as well as a repository (if an automation workflow is activated);
- Associate a test automation server and:
- define default environments for Squash AUTOM servers
- associate jobs for Squash TF servers
Implementation Technology and Script Language
For each project, you can configure the implementation technology of BDD test cases as well as the language of BDD scripts. The project leader can choose between Cucumber and Robot Framework for the implementation technology.
If you select the Cucumber technology, you can choose between the 4 following languages for the script: English, French, Spanish, and German. If you select the Robot Framework technology, English is the only language available.
Automation Workflow
You can activate the automation workflow for a project via a drop-down list.
By default, the "None" option is selected.
Selecting the "Squash advanced" option starts the Advanced Squash Workflow, whereas selecting "Squash simple" starts the Simple Squash Workflow.
When the Jira Automation Workflow plugin is activated for the project, the automation workflow is set to "Remote server".
When you activate an automation workflow, new fields appear in a test case's "Automation" block. For the advanced Squash Workflow, the tests to automate can be tracked in the Automation workspace by both the testers and the automation test writers. For the simple Squash Workflow or the Jira workflow, you can track tests to automate directly from the "Automation" block of the test cases.
When you activate an automation workflow, a new part, "Source code management server" also appears in a project's "Automation" block.
Automated Suite Retention Period
You can set the retention period of the project's automated suites in days. During an automated suite cleaning done by administrator (Administration workspace, System sub-menu), all the automated suites included in the perimeter of that retention period are kept whereas the others are deleted.
If no retention period is set, the automated suites' lifespan is considered as infinite. By default, no value is entered.
Associate a Source Code Management Server
When the automation workflow is activated, the "Source Code Management Server" part appears in the "Automation" block. You must have created a source code management server beforehand, in the Administration workspace > Servers to be able to select it and associate it with a project. Once you have selected the server, the repository names as well as their branch appear in a drop-down list.
You can re-use the Squash TM tree in the repository when you are transmitting the test cases to the source code management tool. Thus, they can be organized in the same way on both sides. You can activate this feature with the field "Use the Squash TM tree in the repository".
Learn More
To learn more about how to create a source code management server, please visit the page Manage Source Code Management Servers
Associate a Test Automation Server
First, you must create a test automation server in the Administration workspace > Servers to associate it with a project.
Learn more
To learn more about creating a test automation server, visit the page Manage Test Automation Servers
Squash AUTOM server
Info
For a project configured with a Squash AUTOM server, if a repository of a source code management server is configured in the project, the Squash AUTOM fields "Automated test technology", "Source code repository URL", and "Automated test reference" are automatically completed when transmitting test cases.
For Squash AUTOM servers ("squashAUTOM" type), once you have selected the server, an "Environment" section appears.
It enables you:
- to indicate which environments are visible by the project
- to view and define default environment tags for the project
- to associate environment variables and define their default values
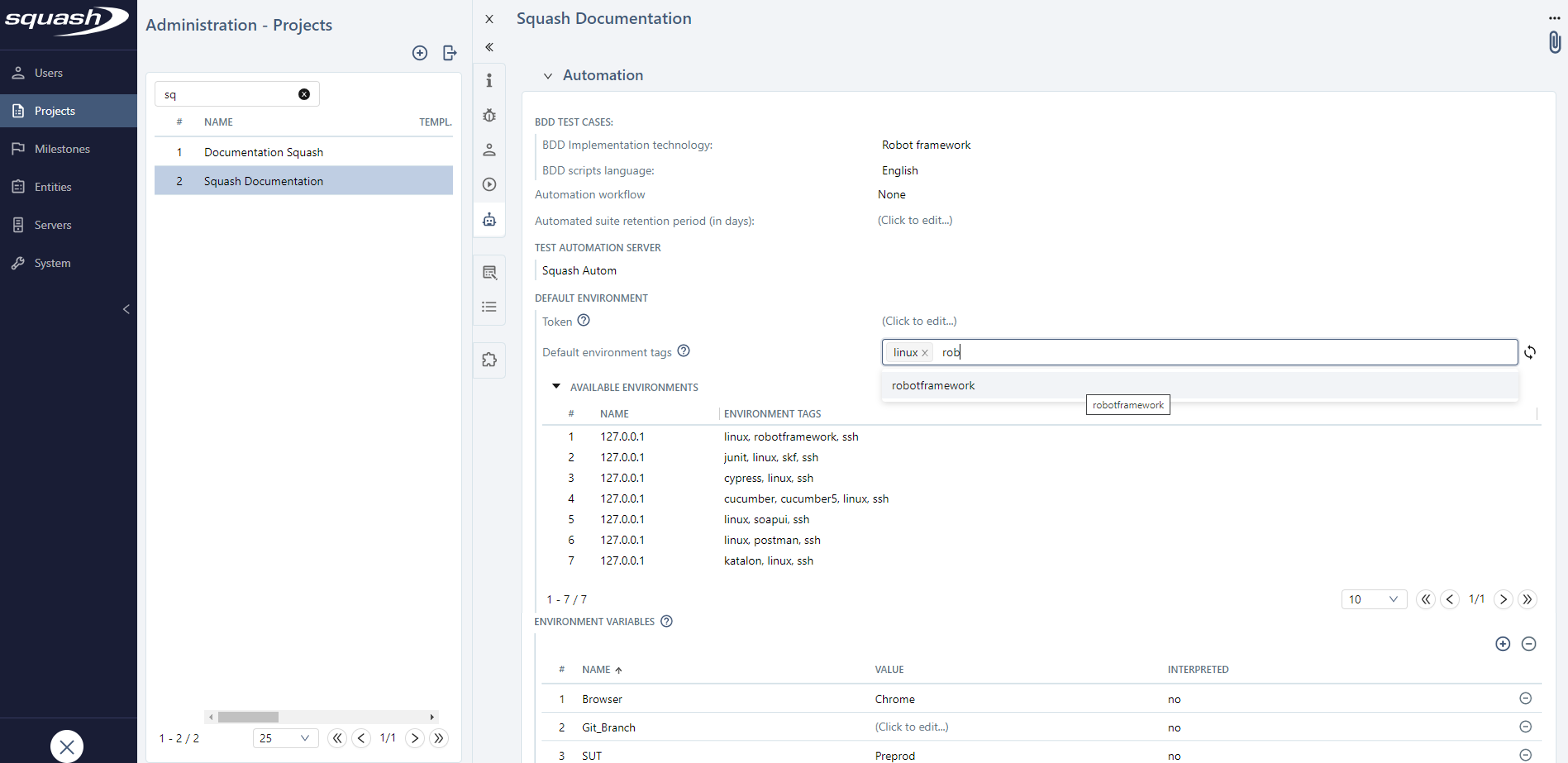
Define environments visible by the project
In Squash Orchestrator, when generating a token, it is possible to grant it permissions to access resources. Depending on the permissions granted, each token can access a set of environments.
Learn more
For more information about token permissions, visit the page [Namespaces] (https://opentestfactory.org/guides/namespaces.html?utm_source=Doc_TM&utm_medium=link){:target="_blank"} on Squash Orchestrator documentation.
In Squash TM, the "token" field enables you to configure a token at the project level. It replaces the one configured for the test automation server linked to the project. This feature enables you to control and compartmentalize access to execution environments for each project.
When this field is empty, the available environment for the project are those accessible by the test automation server's token.
This field is mandatory if there is no token configured for the test automation server.
View and define default environment tags for the projet
The "Default environment tags" field enables you to view and define default values for the project.
If default values are already defined for the test automation server and no token is configured for the project, they are automatically displayed.
However, it is possible to define new defaults values for the project. In this case, these values are offered by default to the user when running automated tests.
If a token is configured for the project, the server's default values are erased and new default values must be defined among the tags of the environments the token has access to.
Associate environment variables and define their default value
In the "Environment variables" section, the environment variables associated with the project are displayed.
From this section, it is possible to associate environment variables with the project and to define their default value.
To associate an environment variable with the project, click on ![]() and select the variable(s) to associate.
and select the variable(s) to associate.
Once the environment associated, it is possible to define a default value. Depending on the environment variable type, different characters are authorized. Only letters, numbers, -, _, . and spaces are allowed.
When running automated tests, this value is offered by default to the user, but he can modify it.
By default, the environment variables associated with the test automation server are automatically associated with the project with their default value, if it exists.
Like environments tags, it is possible to define a new default value of the environment variables for the project.
To dissociate one or multiple environment variable from a project, click on ![]() .
.
Squash TF server
For Squash TF servers ("Jenkins" type), once you have selected the server, you can associate one or multiple jobs with the project.
Info
For a project configured with a Jenkins server, if the repository source code management server configured in the project is identical to the one configured in the job associated with Squash TM and the "Can run BDD" option is checked, automated scripts are automatically associated with the scripted test cases (Gherkin or BDD).
In the Jobs table, only one job can be configured to run BDD scripts.
You can modify a job by clicking on the button  . In the field "Possible execution server(s) (separated by semicolons)", you can choose the secondary servers that will be used to execute the automated test cases. You must fill in the field with the names of the servers separated by semicolons (ex: SecondaryServer1; SecondaryServer2)
. In the field "Possible execution server(s) (separated by semicolons)", you can choose the secondary servers that will be used to execute the automated test cases. You must fill in the field with the names of the servers separated by semicolons (ex: SecondaryServer1; SecondaryServer2)
Customize the Project
Custom Fields
You can manage custom fields from the anchor Custom fields  .
.
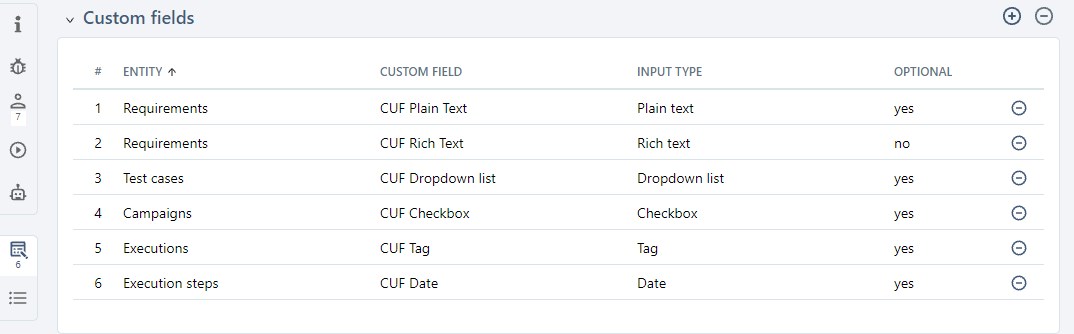
To associate custom fields with a project, you must first create them in the Administration workspace > Entities.
In the table, you can see the custom field's name, type, whether it is optional or mandatory, and the entity with which it is associated.
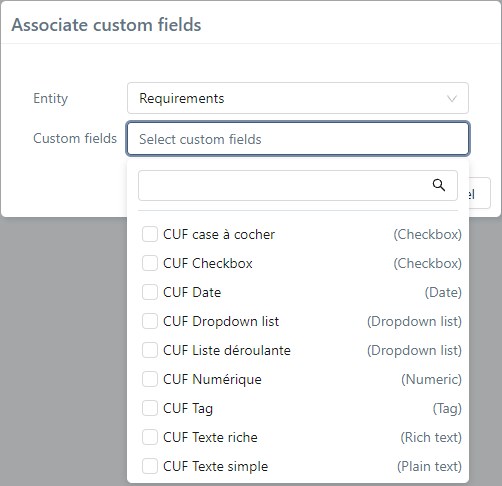
To associate a custom field with the project, click on the button ![]() . In the popup, select the entity and the custom field you want to associate. From there, you can associate multiple custom fields to one entity.
. In the popup, select the entity and the custom field you want to associate. From there, you can associate multiple custom fields to one entity.
One custom field can be associated with multiple entities. Custom fields can be associated with:
-
In the Requirements workspace:
- Requirement folders;
- Requirements.
-
In the Test Cases workspace:
- Test case folders;
- Test cases;
- Test steps.
-
In the Campaigns workspace:
- Campaign folders;
- Campaigns;
- Iterations;
- Test suites;
- Executions;
- Execution steps.
To dissociate one or multiple custom fields for a project, click on the button ![]() .
.
Learn More
To learn more about how to create a custom field, please visit the page Manage Custom Fields.
Information Lists
You can manage information lists from the Information lists anchor  .
.
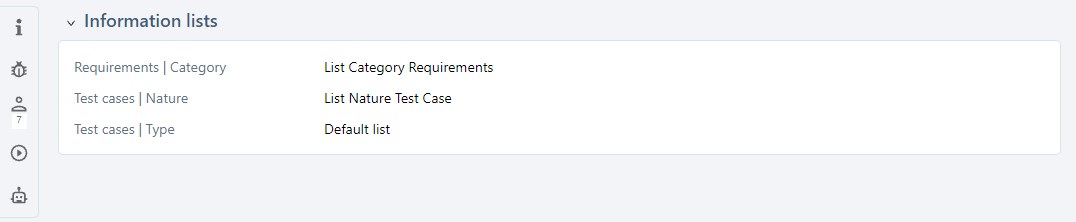
To associate information lists with a project, you must first create them in the Administration workspace > Entities.
An information list can be associated with the "Category" field of requirements, and "Nature" and "Type" fields of a project's test cases. Once the list is associated with the project, in your desired workspace, the values of the field you have chosen will be those of the information list. If you have assigned icons to the values of the list, they will appear in the object's "Information" block.
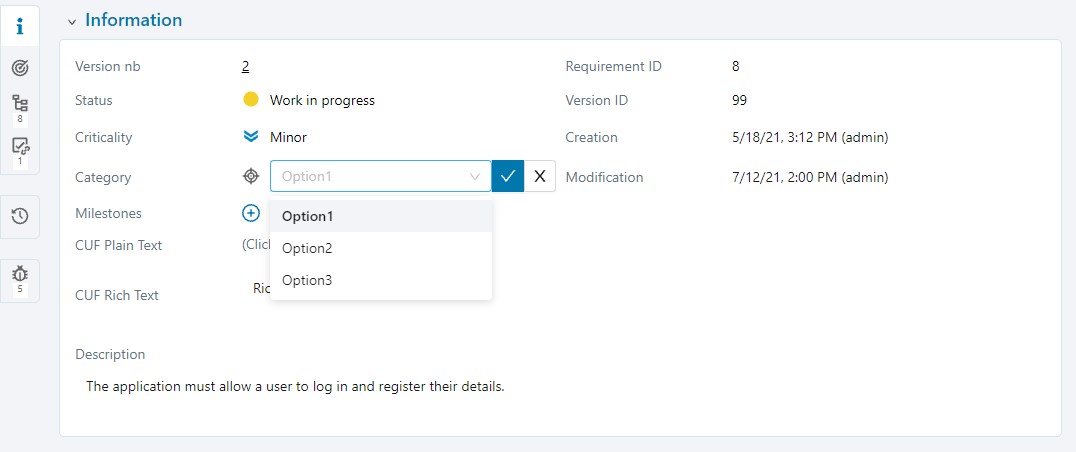
When an information list is associated with a project, the values previously entered are not saved. The default value of the selected list will appear in the field for all the relevant objects.
Learn More
To learn more about how to create information lists, please visit the page Manage information lists
Associate Milestones to a Project
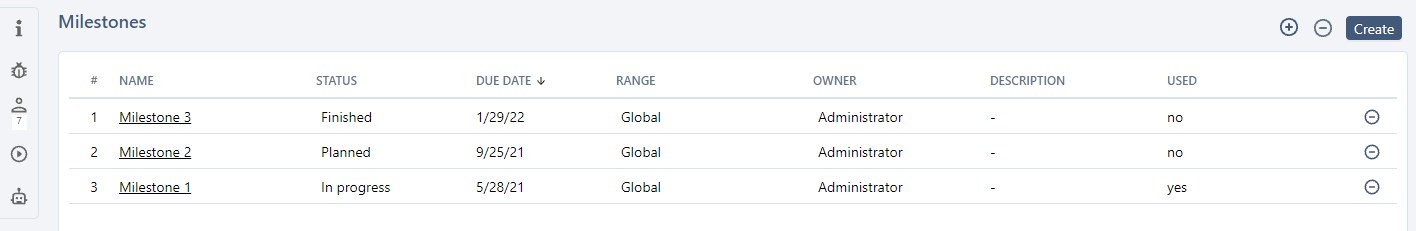
You can associate milestones to a project from the Milestones anchor  .
.
Info
To associate a milestone with a project, the project's status must be "Planned", "In progress", or "Finished".
Associate Milestones with the Button [+]
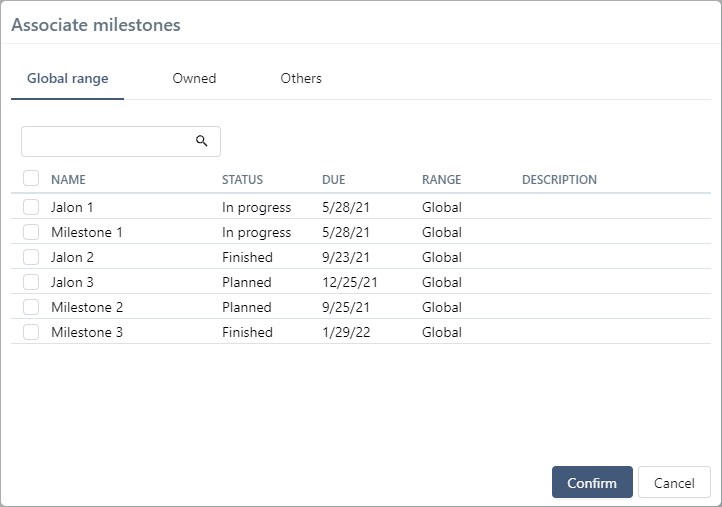
You can associate one or multiple milestones (already created) via the button ![]() . From the associate popup, you can use the search. Milestones are organized by range.
. From the associate popup, you can use the search. Milestones are organized by range.
Associate Milestones with the [Create] Button
If the milestone is not created yet, you can still create it directly from the block using the [Create] button at the top of the table. From the "create" popup, you can then directly associate the milestone you created with the project by clicking on the [Create and associate] button. The created milestone's default status is "In progress".
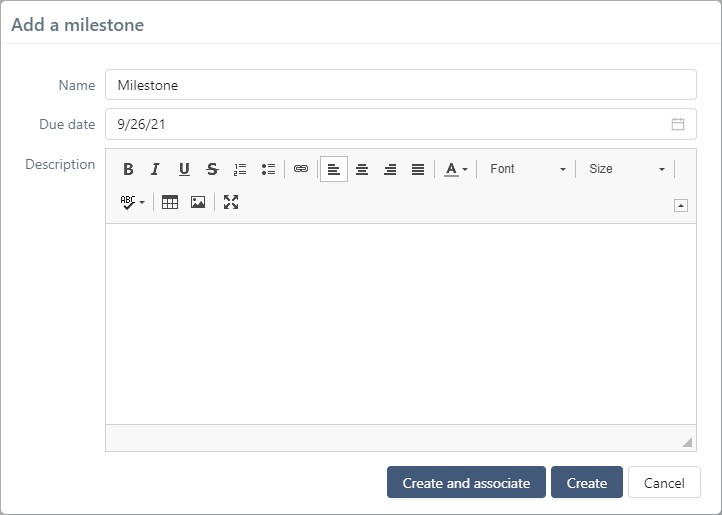
Dissociate Milestones
To dissociate one or multiple milestones from a project, click on the button ![]() available at the end of each row or on top of the table.
available at the end of each row or on top of the table.
After it has been dissociated, the milestone is no longer associated with the project nor the project's objects. The "Used" column indicates if the milestone is associated with objects of the project.
Learn More
To learn more about how to create milestones, please visit the page Manage a Milestone.
To learn more about how to associate a milestone with an object, please visit the page Associate a milestone with an object.