Configure Squash TM for automated tests
Token Authentication
The execution of automated tests from Squash TM uses temporary API tokens. Therefore, the property squash.rest-api.jwt.secret is required to run automated tests with Squash Orchestrator from Squash TM.
Define Squash Public URL
You must imperatively set Squash public URL in the System parameters of the Administration workspace for the execution results of the automated tests executed in the Squash Orchestrator to be transmitted to Squash.
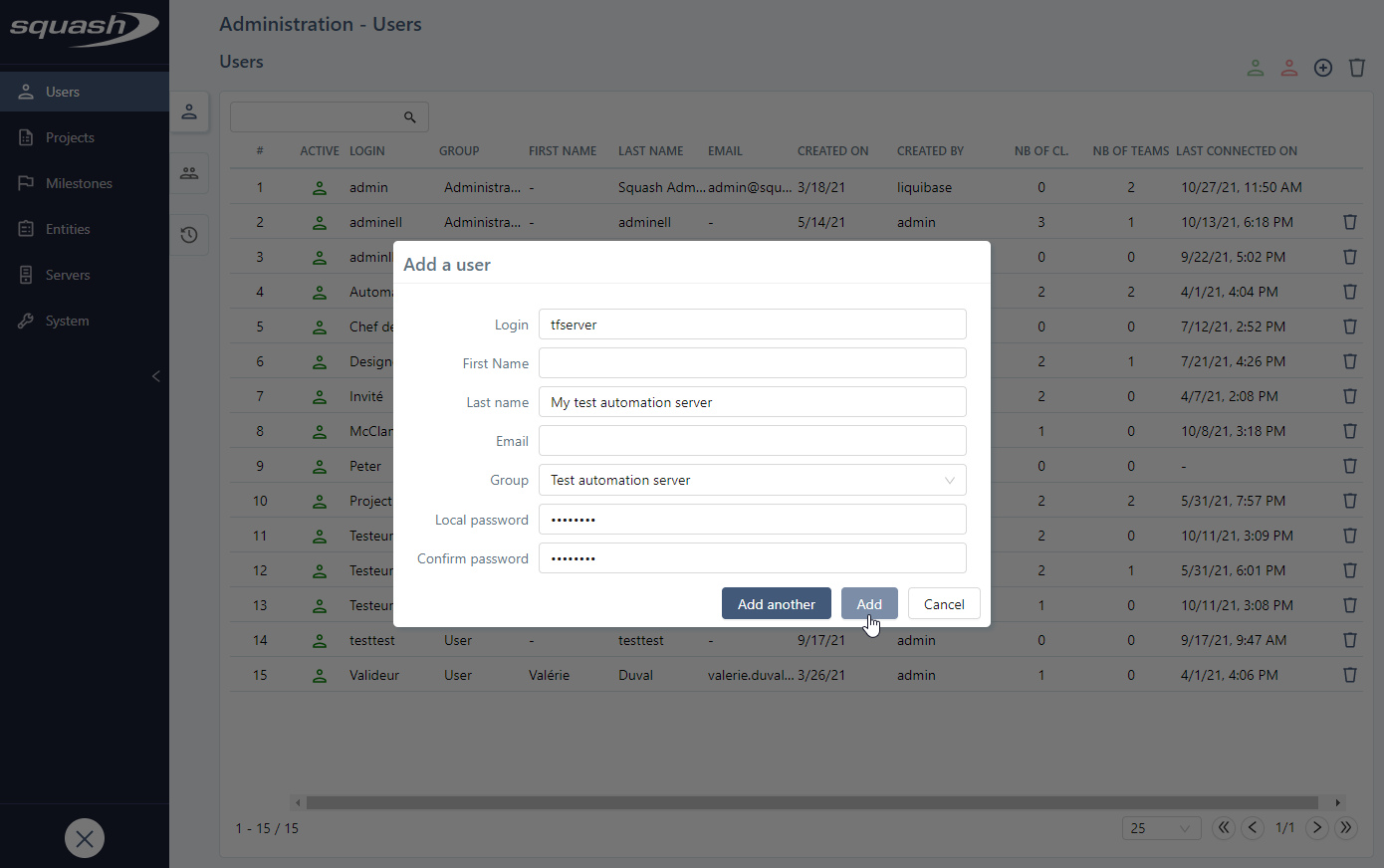
Create a User for the Test Automation Server
To use Squash in DevOps, you must imperatively create a user belonging to the group "Test automation server" in Squash to be able to retrieve a Squash execution plan via a workflow sent from a pipeline. To learn more about how Squash in DevOps operates, please read The Guide to Retrieve a Squash Execution Plan from a workflow.
The creation of a technical user is not mandatory when automated tests are executed from the Squash TM interface (from the Iteration and Suite spaces).
Configure the project
To configure a project, in the Administration workspace, click on the Projects submenu. Click on your desired project to display its consultation page.
Info
Only an administrator or project leader can configure a project.
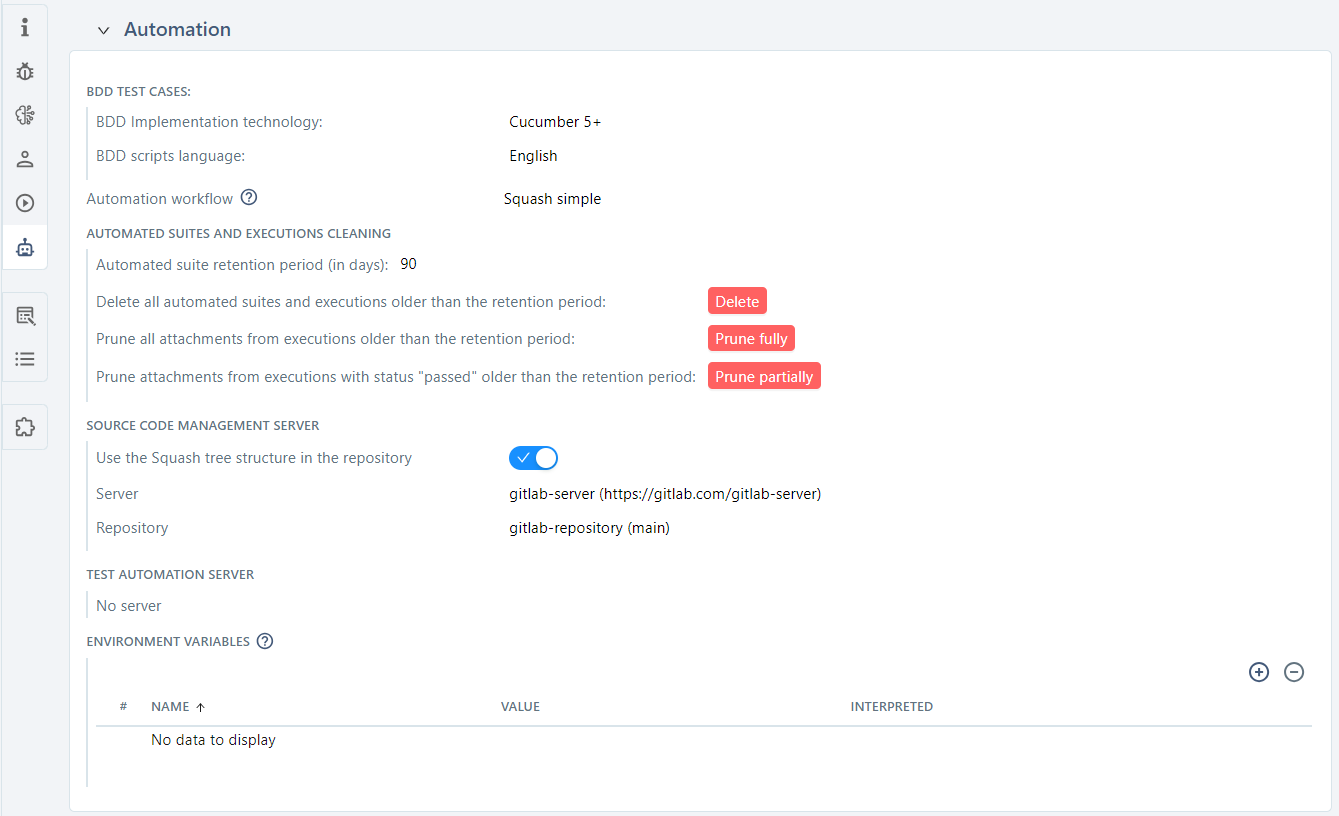
The Automation anchor  enables you to configure the automation of the project.
enables you to configure the automation of the project.
From this block, you can:
- configure the implementation technology and the language of BDD scripts;
- activate an automation workflow (Squash or Jira);
- manage the cleanup of automated suites:
- set a retention period for automated suites;
- delete automated suites;
- delete attachments from executions;
- associate a source code management server as well as a repository (if an automation workflow is activated);
- associate a test automation server and define default environments for Squash Orchestrator servers.
Implementation technology and script language
For each project, you can configure the implementation technology of BDD test cases as well as the language of BDD scripts. The project leader can choose between Cucumber and Robot Framework for the implementation technology.
If you select the Cucumber technology, you can choose between the four following languages for the script: English, French, Spanish, and German.
If you select the Robot Framework technology, English is the only language available.
Automation workflow
You can activate the automation workflow for a project via a drop-down list.
By default, the "None" option is selected.
Selecting the "Squash advanced" option starts the Advanced Squash Workflow, whereas selecting "Squash simple" starts the Simple Squash Workflow.
When the Jira Automation Workflow plugin is activated for the project, the automation workflow is set to "Remote server".
When you activate an automation workflow, new fields appear in a test case's Automation block. For the advanced Squash workflow, the tests to automate can be tracked in the Automation workspace by both the testers and the automation test writers. For the simple Squash workflow or the Jira workflow, you can track tests to automate directly from the Automation block of the test cases.
When you activate an automation workflow, a new part, Source code management server also appears in a project's Automation block.
Automated Suite cleaning
Retention period
The retention period for the project's automated test suites is set in days. During a cleanup (of either automated suites or attachments), all items within this retention period are kept, while others are deleted.
If no retention period is defined, the test suites' lifespan is considered infinite. By default, no value is set.
Deleting Automated Suites
It is possible to delete all automated suites whose creation date is older than the previously defined retention period.
Clicking the [Delete] button opens a confirmation pop-up, indicating that the deletion is permanent and showing a count of the automated suites and executions that will be deleted.
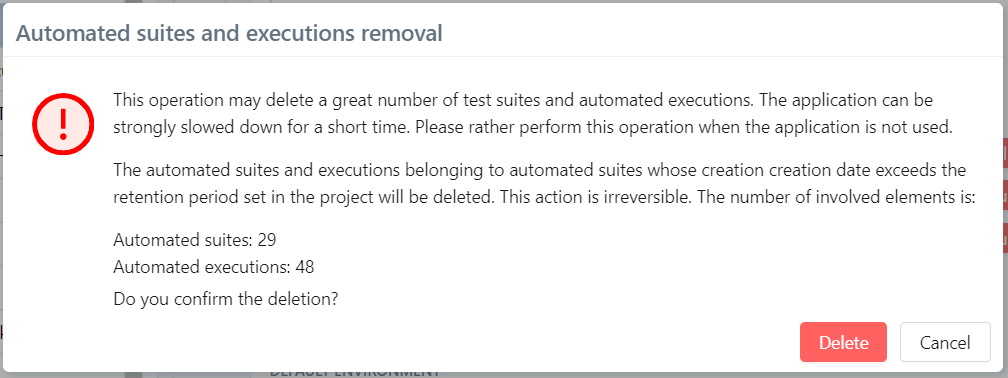
The deletion removes the automated suites as well as everything they contain: executions and attachments.
Deleting Attachments
It is possible to delete all attachments associated with executions of automated suites whose creation date is older than the previously defined retention period.
Clicking the [Prune fully] button opens a confirmation pop-up, indicating that the deletion is permanent, and that it concerns all attachments associated with executions (including execution reports for test cases whose status is not passed).
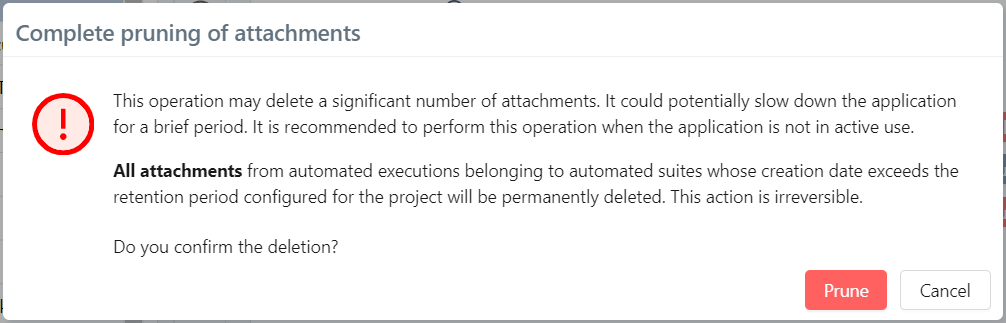
It is possible to delete attachments associated with executions with passed status of automated suites whose creation date is older than the previously defined retention period.
Clicking the [Prune partially] button opens a confirmation pop-up, indicating that the deletion is permanent and only concerns attachments associated with executions whose status is passed.

Associate a Source Code Management server
When the automation workflow is activated, the Source Code Management Server section appears in the Automation block. You must have created a source code management server beforehand, in the Administration workspace > Servers to be able to select it and associate it with a project. Once you have selected the server, the repository names as well as their branch appear in a drop-down list.
You can re-use the Squash tree in the repository when you are transmitting the test cases to the source code management tool. Thus, they can be organized in the same way on both sides. You can activate this feature with the field Use the Squash tree structure in the repository.
Learn More
To learn more about how to create a source code management server, please visit the page Manage Source Code Management Servers.
Info
For a project configured with a Squash Orchestrator server, if a repository of a source code management server is configured in the project, the Automated test technology, Source code repository URL, and Automated test reference fields are automatically completed when transmitting test cases.
Associate a Test Automation server
Simply select the desired server from the dropdown list of the Test automation server field and confirm the choice so that the automated tests of the project can be executed with it.
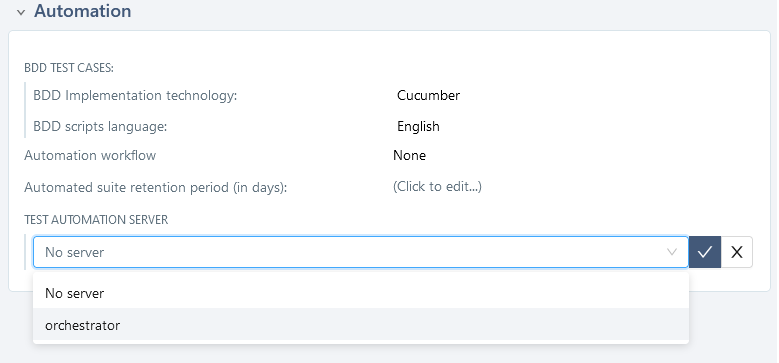
First, you must create a test automation server in the Administration workspace > Servers to associate it with a project.
Learn more
To learn more about creating a test automation server, visit the page Manage Test Automation Servers.
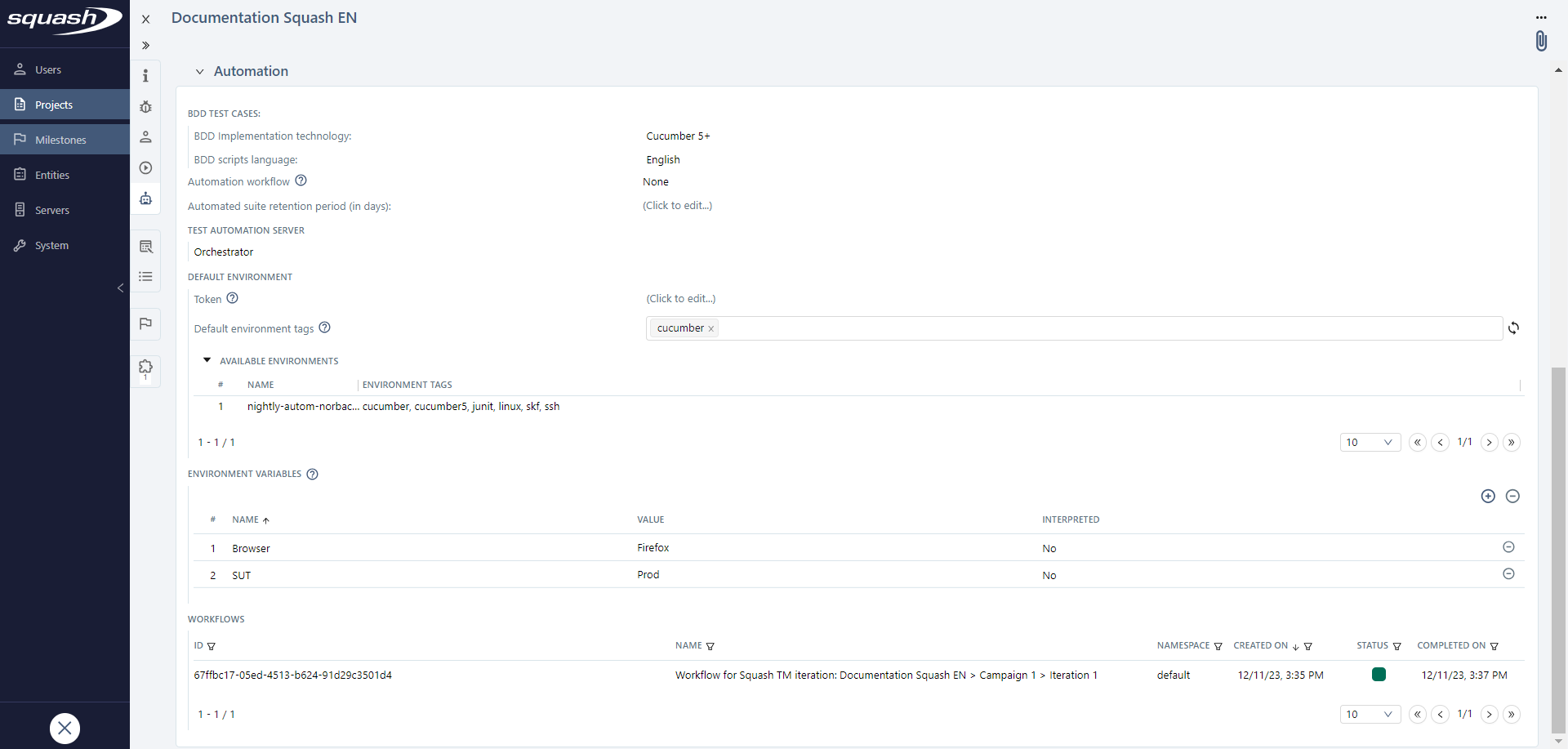
For Squash Orchestrator servers ("Squash Orchestrator" type), once you have selected the server, an environment section appears.
It enables you to:
- indicate which environments are visible by the project;
- view and define default environment tags for the project;
- associate environment variables and define their default values;
- retrieve information on the workflows executed in the project.
Define environments visible by the project
In Squash Orchestrator, when generating a token, it is possible to grant it permissions to access resources. Depending on the permissions granted, each token can access a set of environments.
Learn more
For more information about token permissions, visit the page Namespaces on Squash Orchestrator documentation.
In Squash, the Token field enables you to configure a token at the project level. It replaces the one configured for the test automation server linked to the project. This feature enables you to control and compartmentalize access to execution environments for each project.
When this field is empty, the available environment for the project are those accessible by the test automation server's token.
This field is mandatory if there is no token configured for the test automation server.
View and define default environment tags for the projet
The Default environment tags field enables you to view and define default values for the project.
If default values are already defined for the test automation server and no token is configured for the project, they are automatically displayed.
However, it is possible to define new defaults values for the project. In this case, these values are offered by default to the user when running automated tests.
If a token is configured for the project, the server's default values are erased and new default values must be defined among the tags of the environments the token has access to.
Associate environment variables and define their default value
In the Environment variables section, the environment variables associated with the project are displayed.
From this section, it is possible to associate environment variables with the project and to define their default value.
To associate an environment variable with the project, click on ![]() and select the variable(s) to associate.
and select the variable(s) to associate.
Once the environment associated, it is possible to define a default value. Depending on the environment variable type, different characters are authorized.
When running automated tests, this value is suggested by default to the user, but they can modify it.
By default, the environment variables associated with the test automation server are automatically associated with the project with their default value, if it exists.
Like environments tags, it is possible to define a new default value of the environment variables for the project.
To dissociate one or multiple environment variable from a project, click on ![]() .
.