Execution workspace objects
The Execution workspace comprises two types of object:
- campaigns, iterations and test suites: used for traditional testing methodologies and to execute tests at release level, particularly non-regression tests, in agile methodologies;
- sprints: used in the Scrum methodology, for testing at sprint level.
Both types can coexist within the same project in the Execution workspace.
What are Campaigns, Iterations, and Test Suites?
In SquashTM, the execution phase or "campaign" is ruled as such:
- a campaign starts at the first development delivery and ends at the beginning of production;
- a campaign (or execution phase) is divided into iterations (or cycles);
- each iteration is defined by the amount of time between two development deliveries (evolutions and/or corrections).
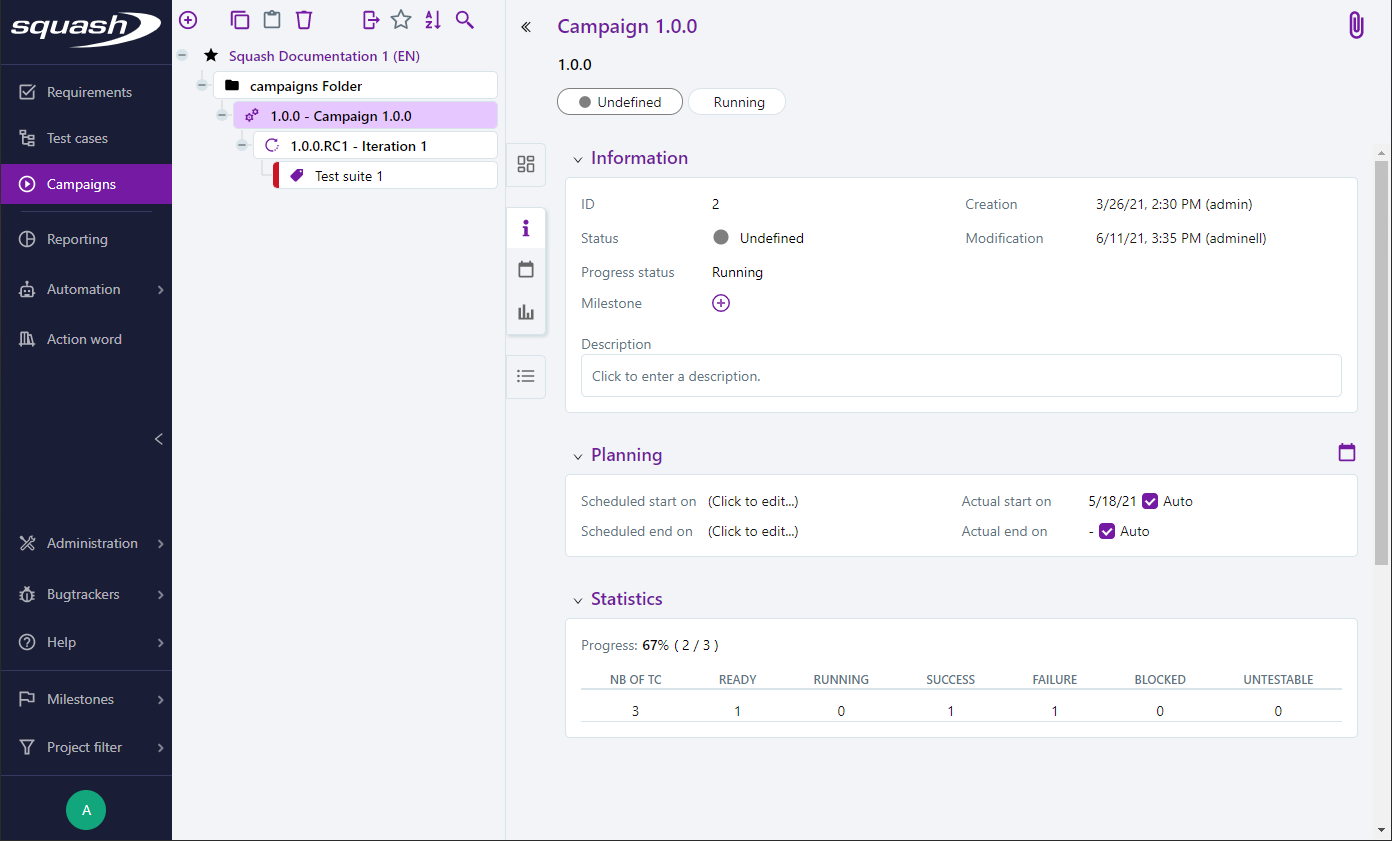
Campaigns
Campaigns are defined by their tag, reference, and execution start and end dates. When the checkboxes Auto are checked, the first and last execution dates are automatically filled.
Their purpose is organizational. While it is possible to feed your execution plan with test cases, you cannot execute tests from a campaign.
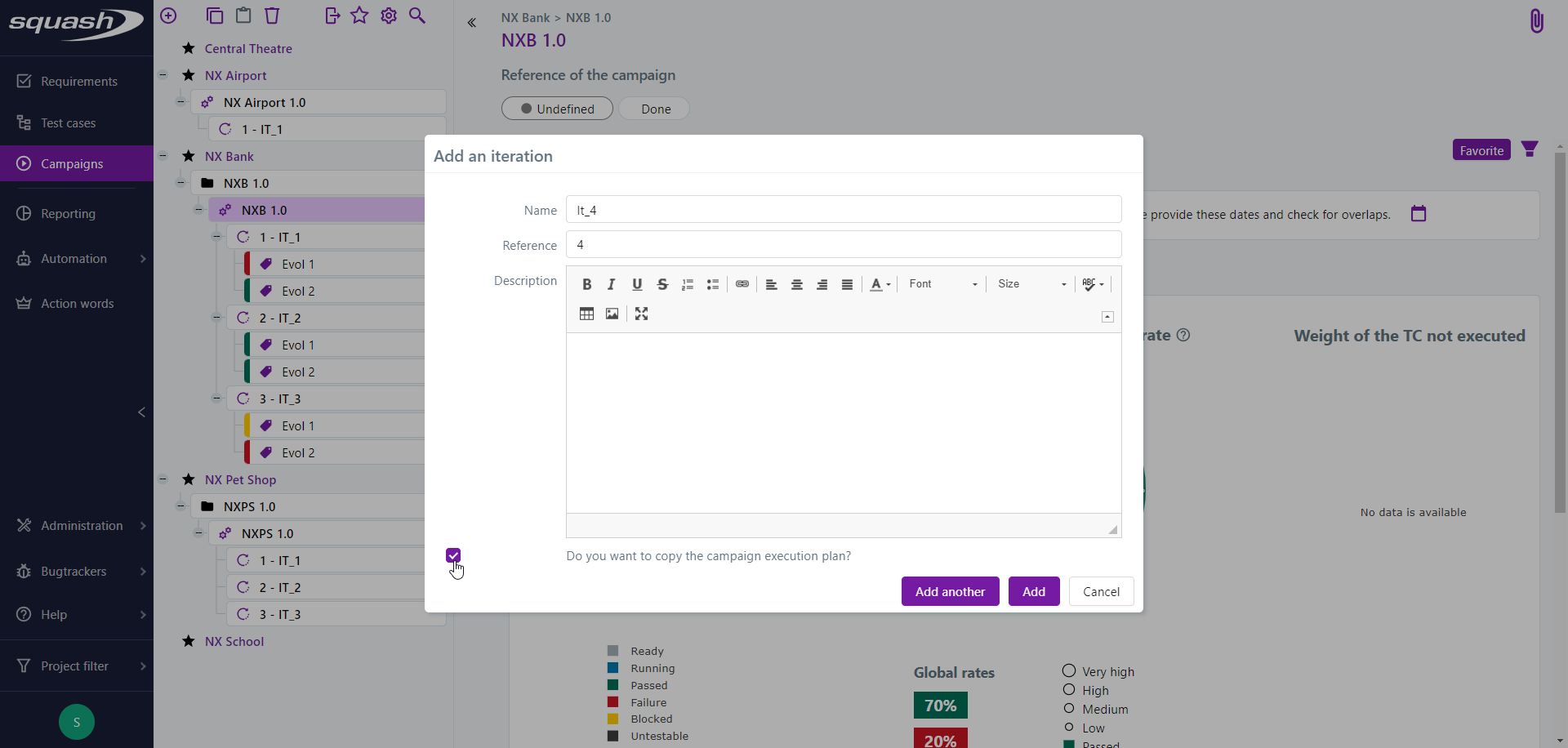
Iterations
Iterations are also defined by their tag, reference, description, execution start and end dates, and a test plan.
They are said to be "operational" because they allow you, from their test plan, to execute the linked tests.
When you create an iteration for a campaign, the test cases that are in the campaign's execution plan can be added to the iteration's execution plan.
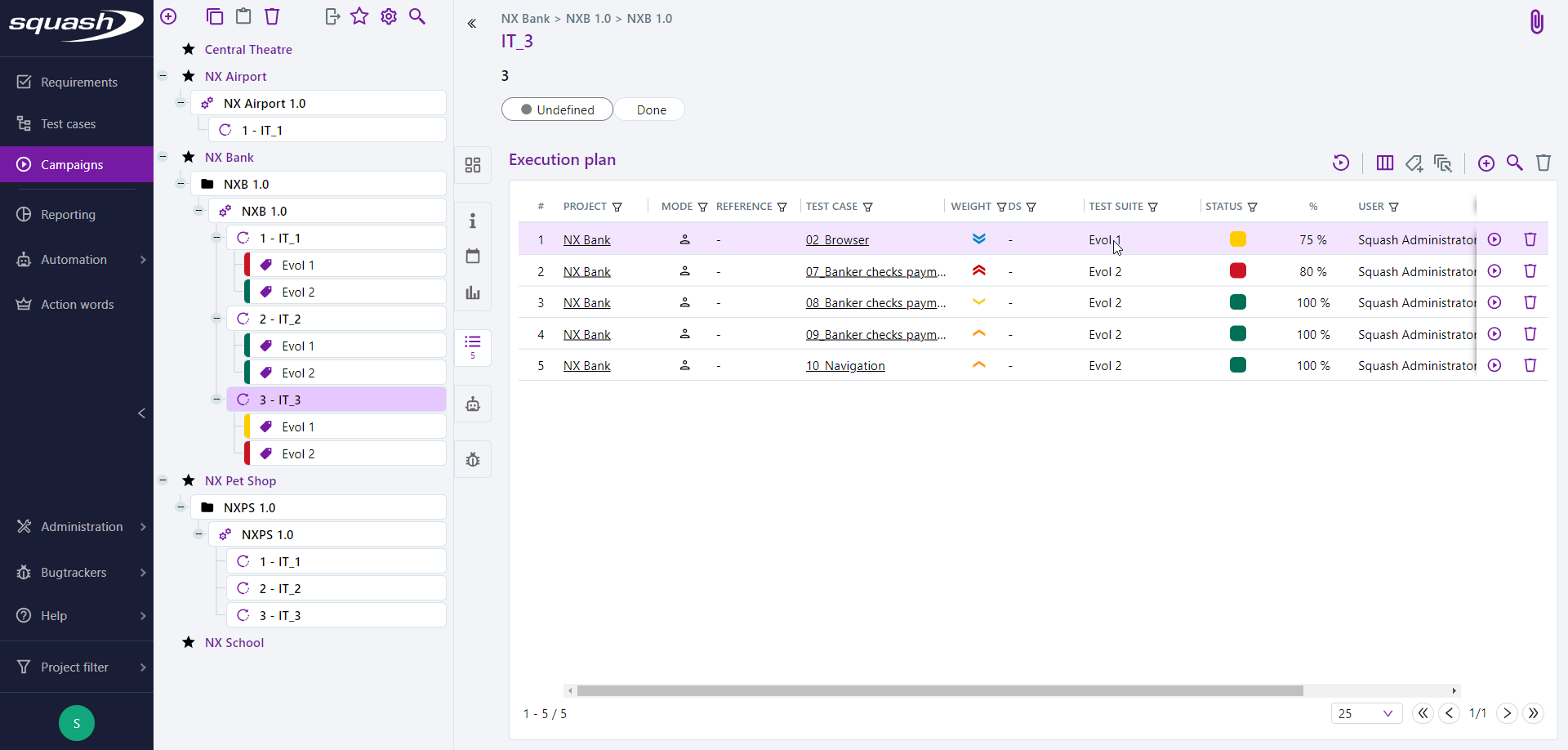
Suites
Suites allow you to organize the execution plans of iterations. They are there to reorganize tests by feature or type.
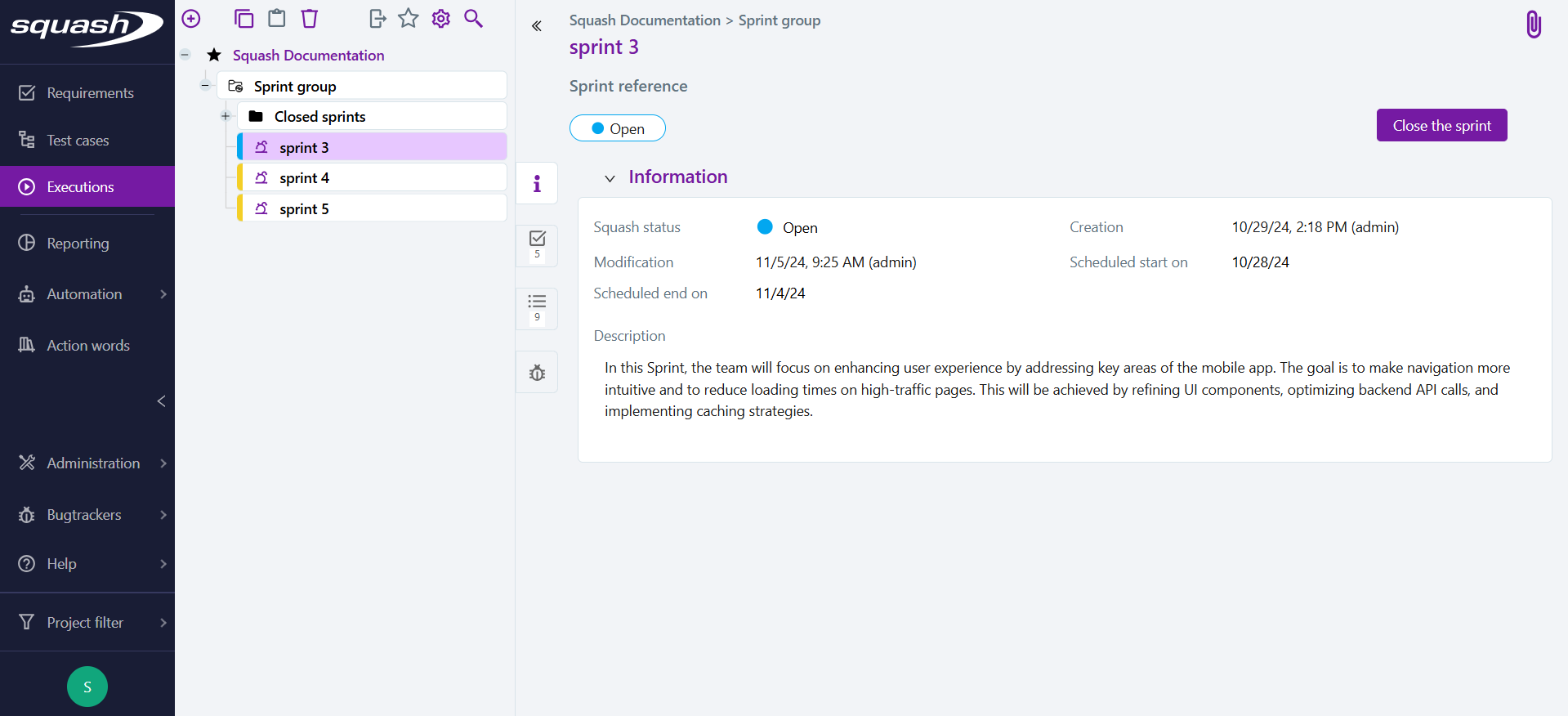
What is a Sprint?
The Sprint object in SquashTM corresponds to the sprint as defined in the Scrum methodology, i.e. a well-defined period during which the development team works to deliver a set of features or improvements in a short cycle.
A sprint is defined by a name, a reference, a description, a status and start and end dates. It contains requirements and an execution plan.